- +1
【CCPR专栏】Open Access | 城市用地功能混合测度方法的比较研究
以下文章来源于CCPR城市规划英文版 ,作者CCPR

CCPR城市规划英文版.
China City Planning Review (《城市规划(英文版)》)创刊于1985年,为中国城市规划学会会刊,国内城市规划领域唯一全英文期刊,致力于向国外读者介绍国内本领域最新学术研究成果。
导读
由中国城市规划学会主办的《China City Planning Review》(CCPR),中文刊名《城市规划(英文版)》,是EBSCO 收录期刊、CSCD 核心库收录期刊、CNKI 全文收录期刊、ProQuest 收录期刊。从本期开始,“中国城市规划”将联手“ CCPR”为读者打造双语专栏,拓宽内容广度。
本文字数:2887字
阅读时间:9分钟


文章题目
城市用地功能混合测度方法的比较研究
A Comparative Study on the Measurement Methods of Urban Mixed Land Use
作者
赵广英,宋聚生,刘淑娟
ZHAO Guangying, SONG Jusheng, LIU Shujuan
文章介绍
有关用地功能混合测度的研究基本围绕功能数量和距离两个方面的核心内容展开,现有的研究方法主要有三类。①多样性视角,根据不同用地类型、功能的面积比例直接计算混合度,或借助辛普森指数(Simpson index)、香农—威纳指数(Shannon-Weaver index)、熵指数(Entropy Index)、碎化指数(Fragmentation Index)、分异指数(Dissimilarity Index)等多样性指标计算混合度。②可达性视角,从不同用地、功能的空间使用需求着手,计算之间的可达性,评价混合程度。③综合多样性和可达性指标,运用指标体系、框架评价混合度。此外,用地功能混合的测度还有赫芬达尔·赫希曼指数(Herfindahl Hirschman index)、阿特金森指数(Atkinson index)、基尼系数(Gini index)和混合指数(mixed-use index)等指数法,对城市空间功能的混合问题适用性较差,多与上述方法结合使用。
探讨地块内建筑功能布局的差异,研究各功能平面、竖向布局差异带来的混合度变化,是改善用地功能混合测度的准确性、适用性的重要途径。从用地功能混合的规划机理来看,中微观尺度的用地功能混合度,主要受功能数量、平面和竖向维度的穿插布局关系三个变量的影响。在空间分析粒度确定,其它变量不变的情况下,单位地块或建筑(对应栅格)内所拥有的功能类型数量越多,混合度越高;竖向上各类功能叠合情况越复杂、面积构成比例越均衡,混合度越高;同样,平面上栅格用地性质与周边相邻栅格用地性质差异越大,混合程度越高。
分析比较典型的城市用地功能混合测度模型发现:①各类测度模型多适用于组团、片区、街区层面的整体混合度测度,栅格粒度的划分宜等于或小于地块面积;②熵指数法、碎化指数法受栅格大小影响较大,栅格粒度宜小于地块,以接近单栋建筑物的平面投影为宜;③机会累积模型和潜力模型等可达性法,考虑了空间的实际需求,更适用于测度“社区生活圈”层面的混合度;④两种分异度模型均比较适用于测度居住、非居住功能的混合程度;⑤空间信息熵、碎化指数法、可达性法可用于具体地块(栅格)的混合测度;⑥各指数类测度方法均无法充分体现栅格内部的功能构成和立体布局带来的混合差异;⑦测度方法之间存在逻辑差异,测度结果彼此缺乏可比性,无法形成统一的指标评价体系。
总之,现有的各类测度方法多借鉴于数学、生态学、地理学等相关学科,在微观的城市用地功能混合测度方面,不能真实、客观地反映建筑功能布局的复杂性和竖向布局特点,也未形成有利于规划评价评估、审批管理的测度指标,与日趋精细化的技术管理需求存在巨大差距。因而,难以实现对控制性详细规划、城市设计管理等具体性、实施性规划的有效指导。在城市用地功能混合测度方法的改进中,探讨地块或建筑物对应的栅格内部建筑功能构成、立体布局和面积比例差异带来的混合度变化,改进片区整体测度模型,是规划领域重要的研究方向。
就用地功能混合本身的内涵而言,影响混合测度的向量主要包括单位面积内功能类型数量、各类功能在平面、竖向组合的结构3个方面。考虑碎化指数法计算结果不受分析粒度的影响,在小尺度、精细化的规划设计中应用简便等特点,平面上可直接用碎化值表达与周边用地功能的差异。此外,现有的测度方法均无法充分体现栅格内部的功能构成和立体布局带来的混合差异,因此,本研究中,竖向上以建筑功能种类数量表达功能丰富程度,以各类功能面积比的标准差表达各类功能的比例均衡性。
Research on the measurement of function mixing of land use basically revolves around two core aspects of function quantity and distance, and there are three main types of existing research methods. ① Diversity perspective. The mixing degree is calculated directly based on the area ratio of different land use types and functions, or with the help of Simpson Index, Shannon-Weaver Index, Entropy Index, Fragmentation Index, Dissimilarity Index and other diversified indicators to calculate the mixing degree. ②Accessibility perspective. Based on the spatial use demand of different land use and functions, the accessibility between them is calculated and the degree of mixing is evaluated. ③Integrated diversity and accessibility indicators. The degree of mixing is evaluated by using the index system and framework.
In addition, there are other index methods such as Herfindahl Hirschman Index, Atkinson Index, Gini Index, and Mixed-use Index, which are less applicable to the function mixing of urban space and are mostly used in combination with the above mentioned methods.
Exploring the differences in the layout of building functions within a plot and studying the changes in the degree of mixing brought about by the differences in the horizontal and vertical layout of each function is an important way to improve the accuracy and applicability of the measurement of the function mixing of land use. From the planning mechanism of function mixing of land use, the mixing degree at the medium and micro-scale is mainly influenced by the variables including the number of functions and the interspersed layout relationships in the horizontal and vertical dimensions. Under the condition that the granularity of spatial analysis is determined and other variables remain unchanged, the more the number of functional types in a unit plot or building (corresponding to a grid), the higher the degree of mixing. The more complex the vertical overlap of various functions and the more balanced the area composition, the higher the degree of mixing; similarly, the greater the difference between the land use property of the grid and the land use property of the neighboring grids on the plane, the higher the degree of mixing.
Analysis and comparison of classic measurement models for function mixing of urban land use reveals that: ① most of the various measurement models are suitable for measuring the overall mixing degree at the cluster, district, and block levels, and the granularity of the grid should be equal to or smaller than the area of the plot; ② the entropy index method and the fragmentation index method are more influenced by the size of the grid, and the granularity of the grid should be smaller than the plot and close to the plan projection of a single building; ③ the cumulative-opportunity model, the potential model, and the other accessibility methods, take into account the actual needs of space, and are more suitable for measuring the mixing degree at the level of "community living circle"; ④ both the two dissimilarity models are more suitable for measuring the mixing degree of residential and non-residential functions; ⑤ spatial information entropy, fragmentation index method and accessibility method can be used for measuring the mixing of specific plots (grids); ⑥ none of the index methods can fully reflect the functional composition and three-dimensional layout of the grids; ⑦ there are logical differences between the measurement methods, and the results are not comparable with each other, so that a unified index evaluation system cannot be formed. In short, the existing measurement methods are mostly borrowed from mathematics, ecology, geography and other related disciplines, which cannot truly and objectively reflect the complexity and vertical layout characteristics of the functional layout of buildings in the microscopic mixed measurement of urban land use, nor do they form measurement indexes that are conducive to planning evaluation and assessment, approval, and management, so there is a huge gap with the increasingly refined technical management needs. As a result, it is difficult to achieve effective guidance for specific and implementation-oriented planning, such as detailed regulatory planning and urban design management. In the improvement of the measurement method for the function mixing of urban land use, it is an important research direction in the field of planning to explore the changes of the mixing degree brought about by the differences in the composition of building functions, three-dimensional layout, and area ratio within the corresponding grids of plots or buildings, and to improve the overall measurement model of the area.
In terms of the connotation of the function mixing of land use, the vectors affecting the measurement of mixing mainly include the number of function types in the unit area and the structure of each type of function in horizontal and vertical combination. Considering that the calculation results of the fragmentation index method are not affected by the granularity of analysis and are easy to apply in small scale and refined planning and design, the fragmentation value can be used directly to express the horizontal difference between the plots and their surrounding land-use functions. In addition, none of the existing measurement methods can fully reflect the functional composition within the grid and the mixed differences brought by the three-dimensional layout. Therefore, in this study, the number of building function types is used to express the functional richness in the vertical direction, and the standard deviation of the area ratio of each type of function is used to express the proportional balance of each function.
关键词
城市规划;用地功能混合;测度;模型;局限性;改进
urban planning; function mixing of land use; measurement; model; limitation; improvement
主要图表
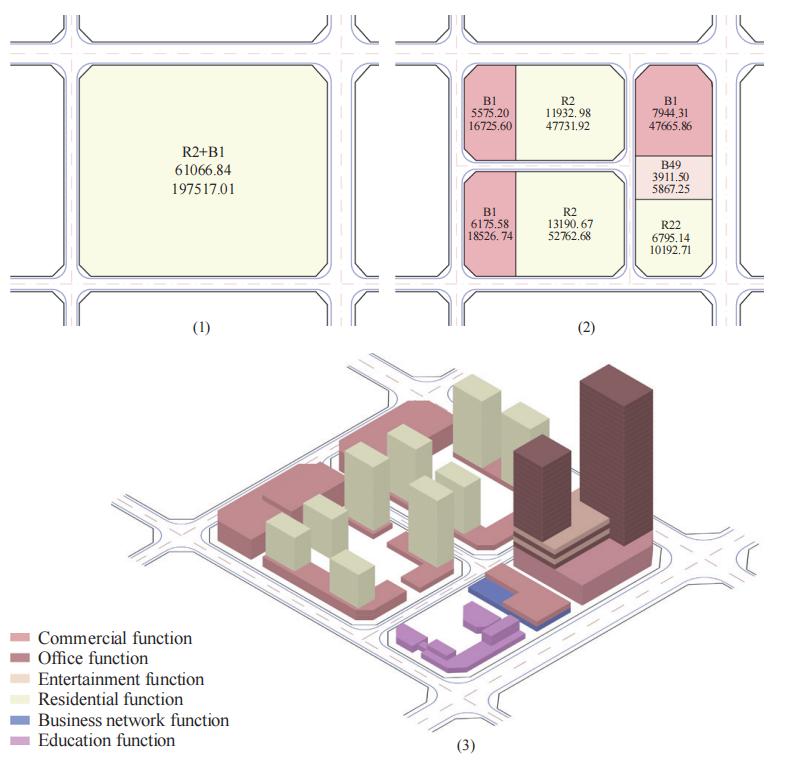
图 1用地功能混合类型
Figure 1 Types of function mixing of land use
Note: In the figure, both scheme (1) and (2) for function mixing control can realize the spatial layout (3). For scheme (1), R2+B1 indicates the mixture of residential land (Category II) and commercial land, allowing the floor area proportion of R2 function ≥ 50% and corresponding proportion of floor area of B1 function ≥ 30% and < 50%. For scheme (2), the single land use R2 indicates that the proportion of floor area of the dominant function (residential) is ≥70%, and the sum of floor area of other compatible functions (commercial and public facilities supporting) is < 30%, and the same is true for the single land use property B1 and B49.

图 3 面积比例法举例
Figure 3 Example of the method of proportion

图 4 熵指数法举例
Figure 4 Example of the method of entropy index
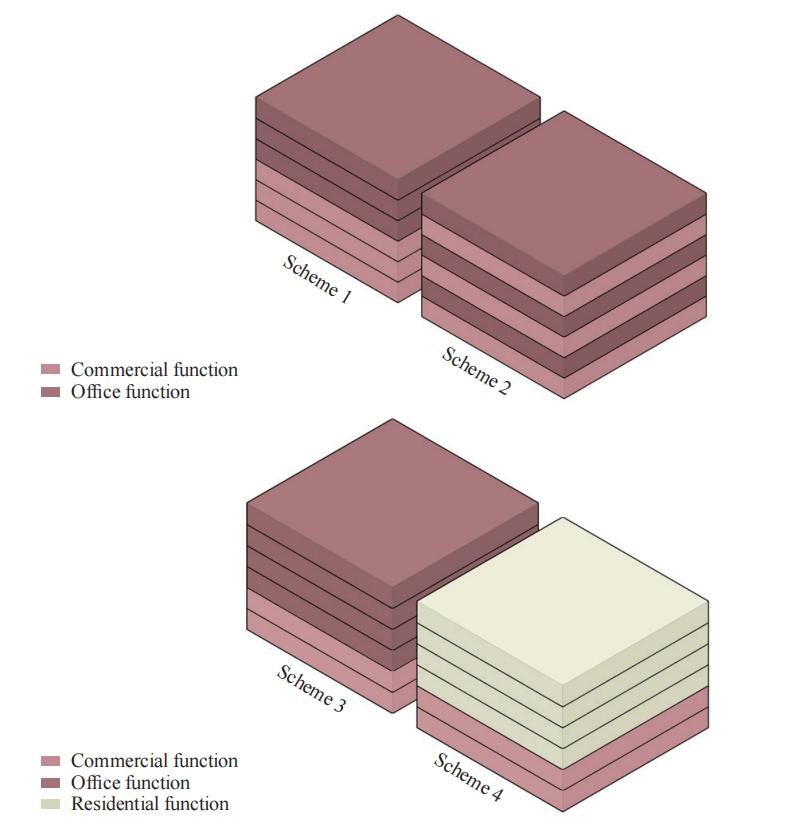
图 5 分异度指数法举例
Figure 5 Example of the method of dissimilarity index
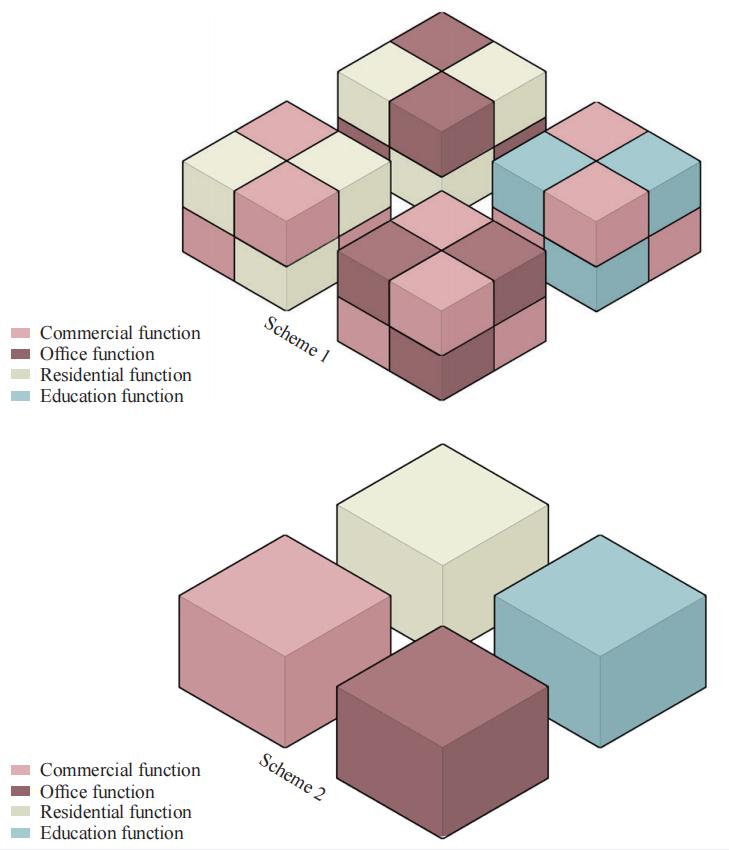
图 6 碎化指数法举例
Figure 6 Example of the method of fragmentation index

图 7用地功能混合测度方法的改进思路
Figure 7 Improving measurement methods for the mixing of land-use functions
作者简介
赵广英,哈尔滨工业大学(深圳),博士研究生;主任工程师,高级规划师。
Zhao Guangying, Senior Planner, PhD Candidate, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, P. R. China. Email: 120668639@qq.com
宋聚生(通讯作者),哈尔滨工业大学(深圳),教授,博士生导师,建筑学院执行院长。
Song Jusheng (corresponding author), Professor, Doctoral Supervisor, School of Architecture, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen, P. R. China.
刘淑娟,广东白云学院建筑工程学院,讲师。
Liu Shujuan, Lecturer, School of Architecture and Engineering, Guangdong Baiyun University, Guangzhou, P. R. China.
全文链接
http://www.ccprjournal.com.cn/news/10155.htm
欢迎您通过以下方式查询购买:
To purchase the new issue of CCPR, please contact us via:
Tel:010-82819550, Email:ccpr@planning.org.cn.
您也可以登陆网站进行文章浏览:
Or you can also read the papers via:
www.ccprjournal.com.cn
扫码关注
CCPR城市规划(英文版)
↓↓↓
China City Planning Review (《城市规划(英文版)》)创刊于1985年,为中国城市规划学会会刊。国内城市规划领域唯一全英文期刊,致力于向国外读者介绍国内本领域最新学术研究成果。
本文来源:CCPR城市规划英文版
【免责声明】本公众号发布的内容仅供学习交流使用,不以任何形式进行牟利。内容版权归原作者所有。如有侵犯您的权益,请及时与我们联系,我们将于第一时间协商版权问题或删除内容。内容为作者个人观点,不代表本公众号立场和对其真实性负责。
你可能还想看这些
《城市规划(英文版)》召开第四届编委会第一次工作会议

点击图片阅读全文

规划界期刊探讨知识产权保护,共同推动期刊出版繁荣

点击图片阅读全文

《城市规划》再次入选“中国最具国际影响力学术期刊”
点击图片阅读全文
原标题:《【CCPR专栏】Open Access | 城市用地功能混合测度方法的比较研究》
本文为澎湃号作者或机构在澎湃新闻上传并发布,仅代表该作者或机构观点,不代表澎湃新闻的观点或立场,澎湃新闻仅提供信息发布平台。申请澎湃号请用电脑访问http://renzheng.thepaper.cn。




- 报料热线: 021-962866
- 报料邮箱: news@thepaper.cn
互联网新闻信息服务许可证:31120170006
增值电信业务经营许可证:沪B2-2017116
© 2014-2024 上海东方报业有限公司




