- +1
Life Medicine 第3卷第1期发布

Life Medcine第3卷第1期
近日,Life medicine第3卷第1期正式在线发布。本期共收录新闻观点(News & Opinion)2篇、亮点(Research Highlight)2篇、论坛(Forum)1篇、综述(Review)2篇、研究长文(Article)2篇以及研究短文(Letter)1篇。

Life Medicine 第3卷第1期封面
On the Cover
Under physiological conditions, the liver possesses a strong potential for repair and regeneration after injury. However, with aging, these potential declines, and factors such as alcohol, drug, toxins, and other harmful substances can accelerate liver aging and induce a series of pathological features associated with aging-related liver diseases. These features include reduced liver volume, decreased blood flow, exacerbated inflammatory responses, and even increased fibrosis. These changes can impair the liver’s regenerative capacity to varying degrees, much like the wilting process of plant veins. A profound understanding of these pathological processes will aid in uncovering the mechanisms of liver aging and aging-related diseases and in exploring strategies to slow aging and promote liver health, allowing the tree of life to remain evergreen.
本期封面
肝脏在生理条件下具有强大的损伤后修复和再生潜能。增龄会让这些潜能下降,酒精、药物、毒物等因素会进一步加快肝脏衰老的进程并诱发肝脏出现一系列衰老相关疾病的病理特征,如肝体积减少、血流量降低、炎症反应加剧,甚至纤维化程度增加等。这些变化不同程度影响肝脏再生能力,正如植物脉络的枯萎过程。深刻理解这些病理过程将助力我们揭示肝脏衰老及衰老相关疾病的机制,并探究延缓衰老促进肝脏健康的策略,让生命之树常青。
1
News & Opinion
Deciphering microbiota-host interplay: bacterial metabolites and protein post-translational modifications
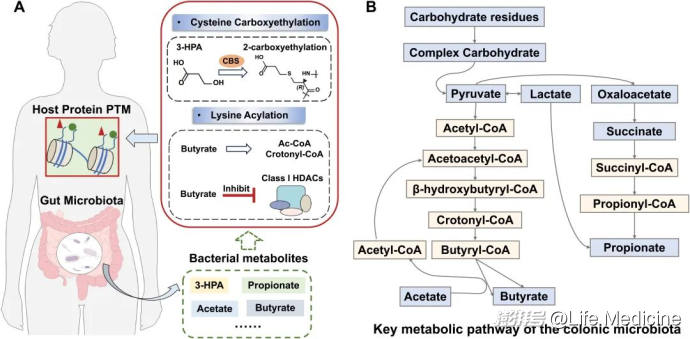
微生物和宿主的相互作用

From clones to synthetic embryos
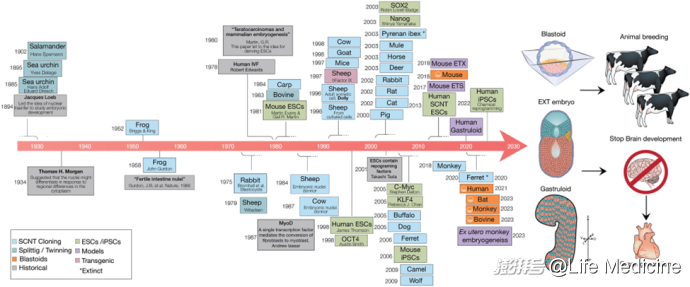
克隆的前世今生和未来应用
2
Research Highlight
Programmable G-to-Y base editing using engineered DNA glycosylase
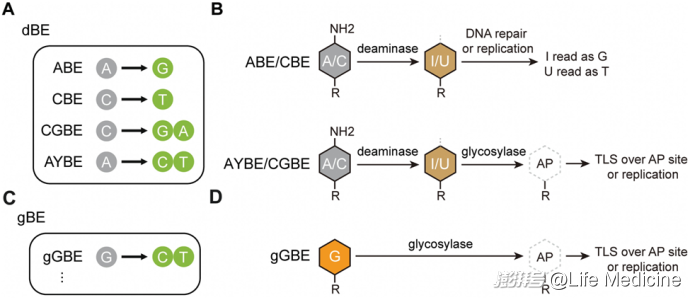
非脱氨酶依赖的新型单碱基编辑工具
Tuning mitochondrial dynamics for aging intervention
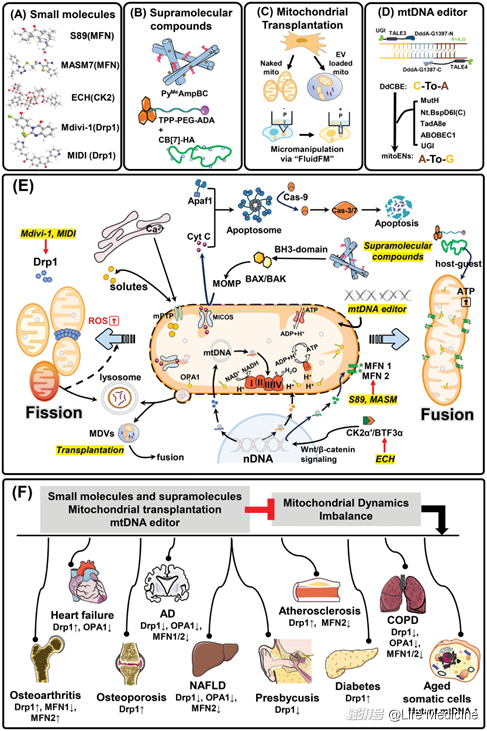
调控线粒体动力学以干预衰老
3
Forum
A biomarker framework for liver aging: the Aging Biomarker Consortium consensus statement
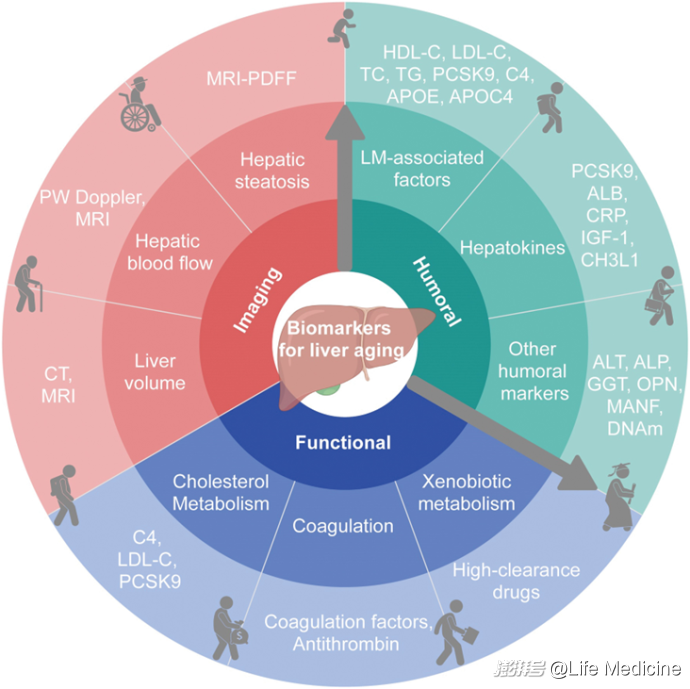
中国衰老标志物联合体发布肝脏衰老标志物专家共识
4
Review
When synthetic biology meets medicine
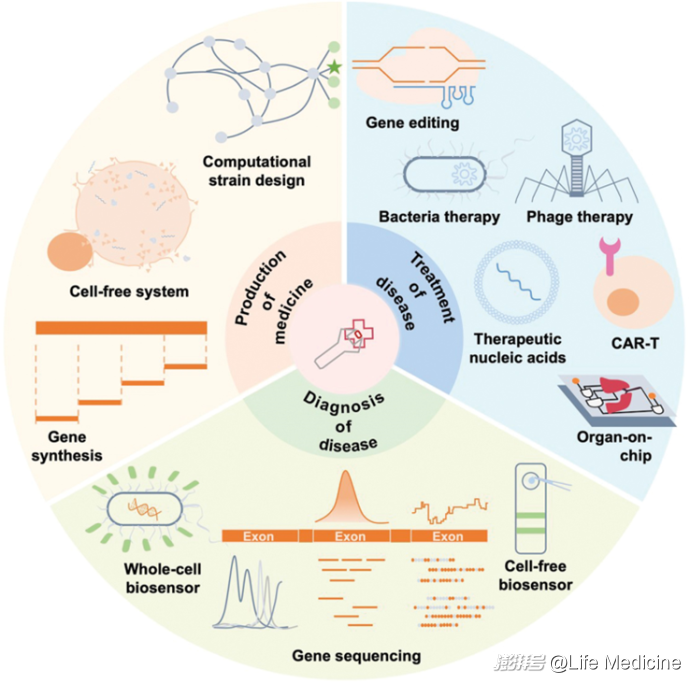
合成生物学与医学
Osteoporosis under psychological stress: mechanisms and therapeutics
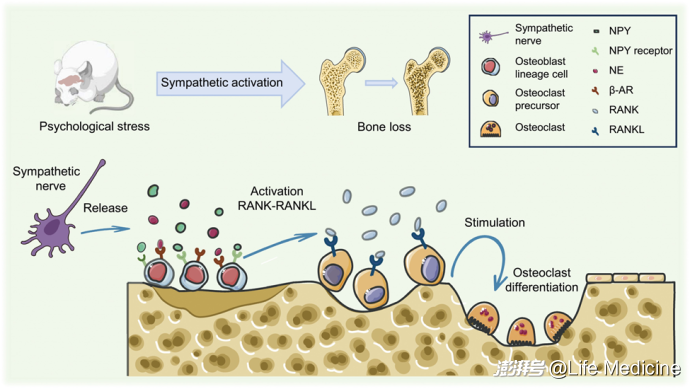
心理应激与骨质疏松的联系与治疗
5
Article
Tracing TMEM106B fibril deposition in aging and Parkinson’s disease with dementia brains
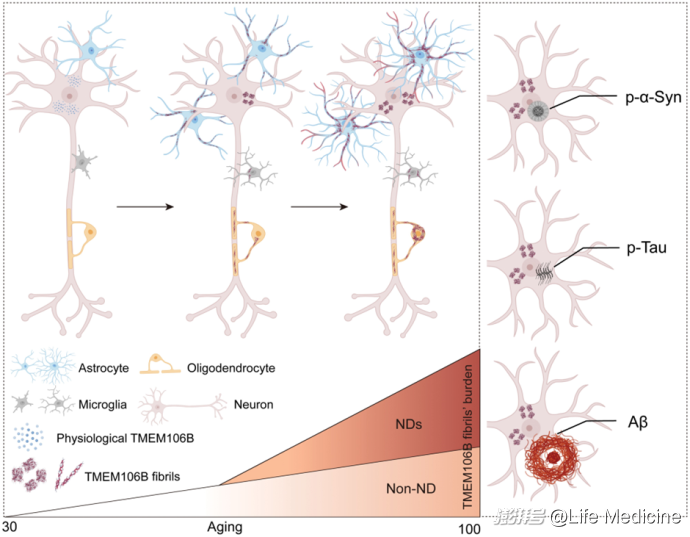
TMEM106B聚集体在衰老和帕金森病痴呆人脑中的特征
Follicular fluid-derived exosomes rejuvenate ovarian aging through miR-320a-3p-mediated FOXQ1 inhibition
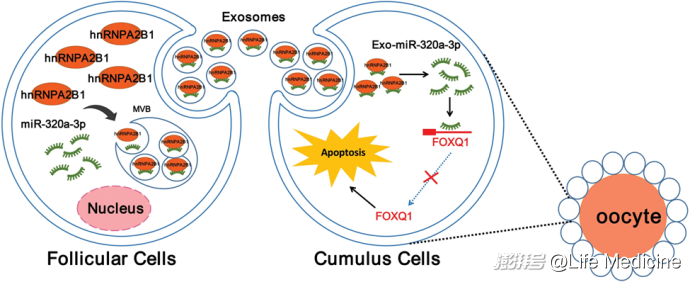
年轻人卵泡液外泌体miR-320a-3p通过靶向FOXQ1延缓卵巢衰老
6
Letter
Modeling antiviral response in the liver using human pluripotent stem cell-derived macrophages
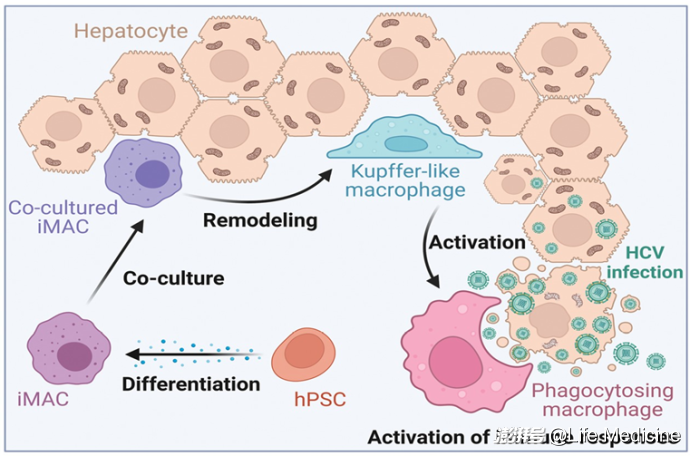
人多能干细胞衍生的巨噬细胞-肝细胞共培养模型研究肝炎病毒感染
Life Medicine第3卷第1期网站链接:
https://academic.oup.com/lifemedi/issue/3/1
本文为澎湃号作者或机构在澎湃新闻上传并发布,仅代表该作者或机构观点,不代表澎湃新闻的观点或立场,澎湃新闻仅提供信息发布平台。申请澎湃号请用电脑访问http://renzheng.thepaper.cn。





- 报料热线: 021-962866
- 报料邮箱: news@thepaper.cn
互联网新闻信息服务许可证:31120170006
增值电信业务经营许可证:沪B2-2017116
© 2014-2026 上海东方报业有限公司




